Fluoropolymers are a class of synthetic polymers that contain fluorine atoms. Among the various types of fluoropolymers, the five commonly used ones are PTFE, PVDF, ETFE, PFA, and FEP. Each of these fluoropolymers offers unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
Comparison Chart
Property | PTFE | PVDF | ETFE | PFA | FEP |
Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
Temperature Range | -200°C ~ 260°C | -40°C ~ 150°C | -200°C ~ 150°C | -200°C ~ 260°C | -200°C ~ 205°C |
Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
Transparency | Opaque | Opaque | Transparent | Opaque | Transparent |
Mechanical Strength | Low | High | Low | Medium | Medium |
UV Resistance | Poor | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
For more details, let’s take a closer look at each of them:
PTFE
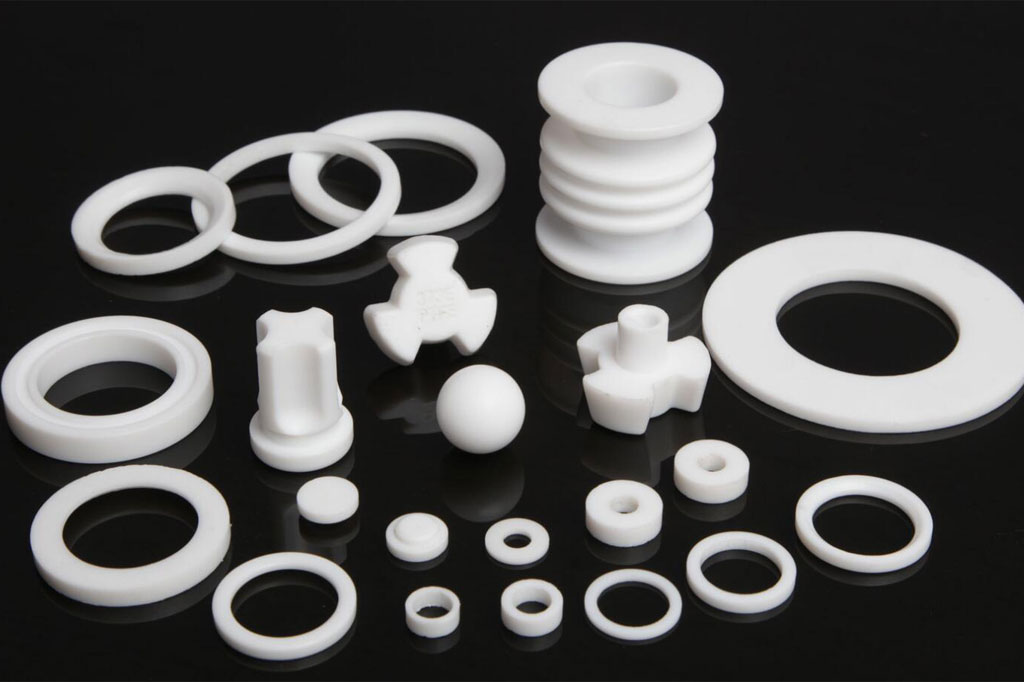

PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is one of the most well-known and widely used fluoropolymers. It is famous for its exceptional non-stick properties, high-temperature resistance (up to 260°C or 500°F), and excellent chemical resistance. PTFE’s low friction coefficient, excellent electrical insulation, and high melting point make it ideal for applications where low friction, chemical resistance, and temperature stability are critical.
|
|
PVDF
PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) is a versatile fluoropolymer that offers a balance of excellent chemical resistance, UV stability, high thermal stability (up to 150°C or 300°F), and good mechanical properties. It is often used in applications where resistance to harsh chemicals, UV radiation, and weathering is required. PVDF finds applications in the chemical industry, oil and gas sector, electrical components, and architectural coatings.
|
|
ETFE
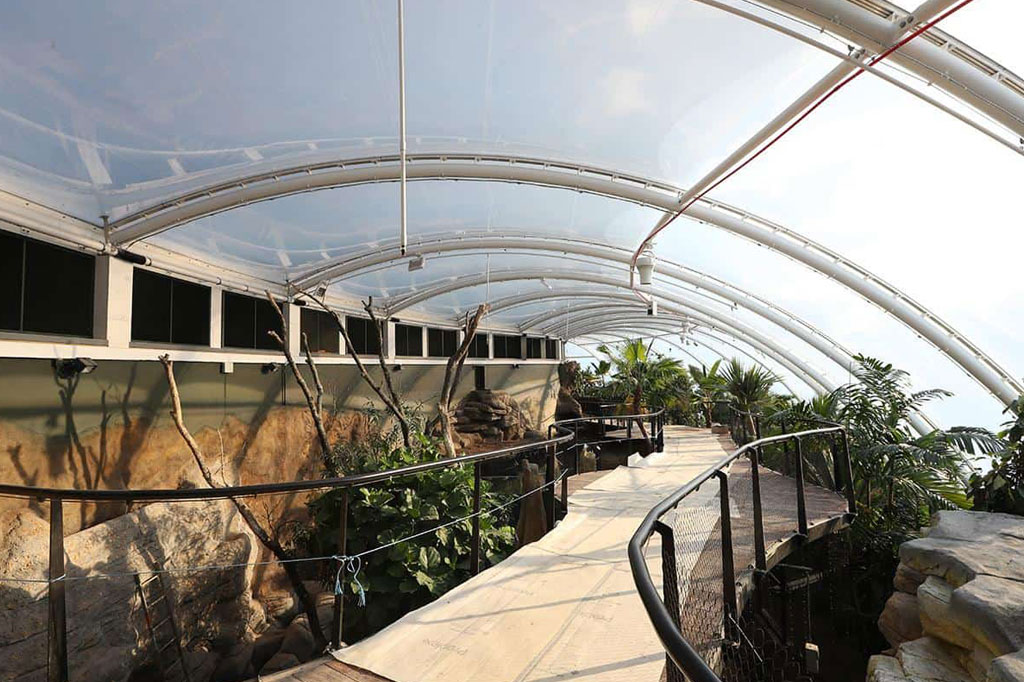

ETFE (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene) is a lightweight and highly transparent fluoropolymer with exceptional electrical properties and excellent resistance to weathering and UV radiation. It has a high melting point (up to 270°C or 518°F) and outstanding mechanical strength. It is widely used in architectural applications, such as roofs and façades, due to its lightweight nature, thermal insulation properties, and ability to transmit natural light. ETFE membrane combines transparency, durability, and weatherability, which makes it an attractive choice for both interior and exterior applications.
|
|
PFA
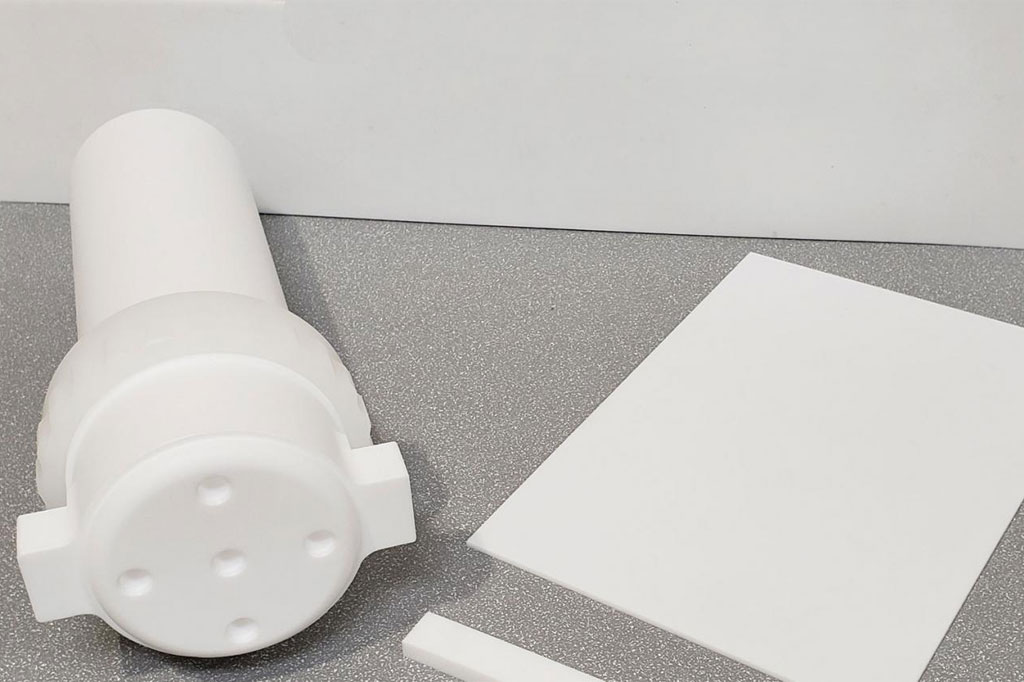

PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) is a melt-processable fluoropolymer that combines the properties of PTFE and FEP. It exhibits excellent chemical resistance, high-temperature stability (up to 260°C or 500°F), low friction, and good electrical insulation properties. PFA is widely used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and electrical components where high purity, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability are crucial.
|
|
FEP
FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) is a fluoropolymer that possesses similar properties to PTFE but can be melt-processed, enabling it to be extruded and molded into various shapes. It offers excellent chemical resistance, a broad temperature range (up to 200°C or 392°F), low friction, and excellent electrical insulation properties. FEP is commonly used as a lining material for pipes, tanks, and vessels, as well as in wire and cable applications.
|
|